What Are Annuities?
An annuity is an insurance contract between you, the owner, and a life insurance company. Here are some fast facts about annuities:
- Life insurance companies issue annuities through contracts. Consumers pay premiums with before- or after-tax dollars.
- The issuer invests the money for you, and any interest earned grows tax deferred.
- At some point, the issuer pays out the balance and interest to you or your beneficiaries.
- Interest is taxed as ordinary income when distributed. If premiums were paid with before tax money, the principal and interest are both taxed as income when the funds in the annuity are distributed (an additional 10% tax will apply to funds withdrawn prior to age 59 1/2).
- Withdrawals are subject to income tax, and if made before age 59½, may have a 10% penalty tax.
The primary features of annuities are tax-deferred accumulation potential and distribution options that can provide a steady stream of income that can last for a certain time period or for life. It can supplement retirement income sources such as Social Security, pension plans, or 401(k)s. Annuities can also help you achieve long-term goals such as providing a legacy for your heirs or making a charitable gift.
Are annuities right for your retirement plan? Let’s dive in further.
Main Types of Annuities
There are three main types of annuities – fixed, fixed index, and variable.
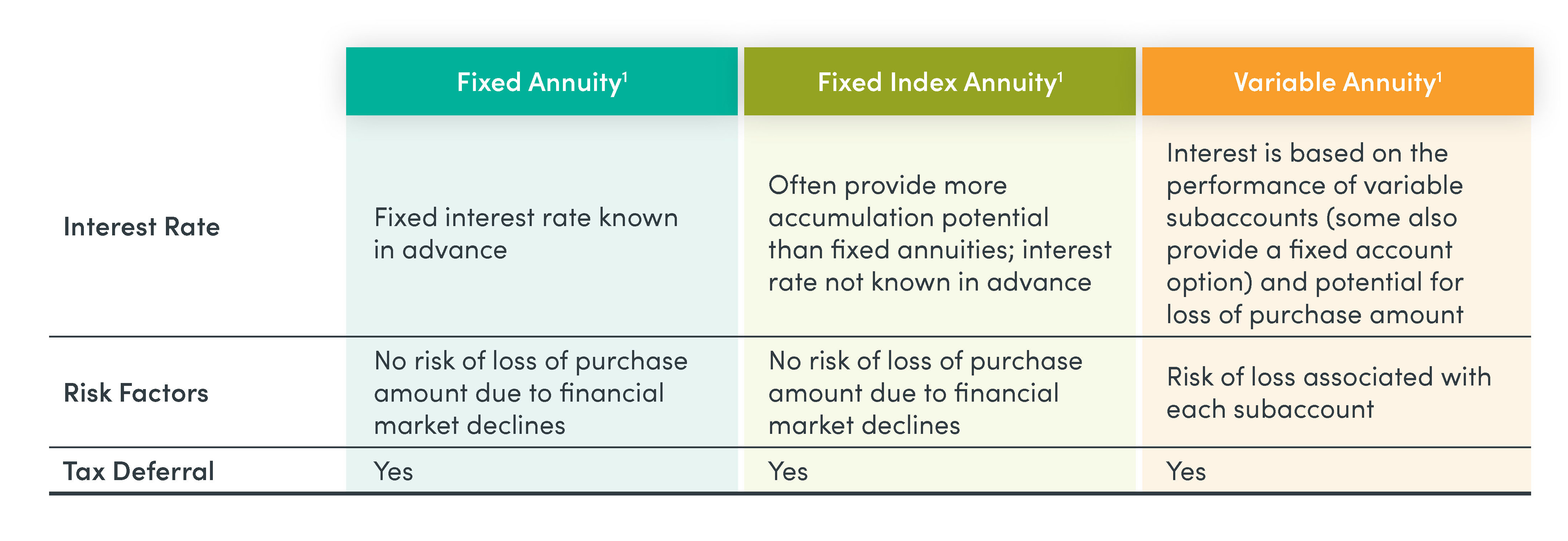
Fixed annuities guarantee the principal cannot decrease due to market declines. What’s more, the issuer provides a Guaranteed Minimum Interest Rate (GMIR) on your annuity.1 The issuer’s money managers invest and manage your contract which are part of the issuer’s general assets and subject to creditor claims. You should be aware of this risk when buying fixed annuities.
A fixed index annuity (FIA) protects from losses in a down market and offers an opportunity for interest based on part of the positive change in or more financial indexes. You can buy the annuity in one payment or a series of premium payments, depending on the product and its terms. Interest credited to your account cannot be lost, which allows for compounding of interest. Your interest credits are based on an external underlying index, for example, the S&P 500® Index. The insurance company uses a formula to determine interest based on the performance of the index crediting options.
A variable annuity offers no guarantees unless there is a fixed account option. You assume all risk relating to the performance of the underlying investments. You could lose money if the investments perform poorly.
Fees and Expenses
Some fixed annuities and FIAs may charge an annual contract fee and/or a charge for certain additional benefits. Also, variable annuities may:
- Assess mortality and expense risk charges.
- Include investment fees and operational costs for subaccounts.
Annuities may have surrender charges if you withdraw early, usually in the first 5-10 years. Also, a market value adjustment may apply (which may be positive or negative), and you may lose any bonus credited to your contract.
Taking Money Out of Your Annuity
There are generally two ways you can take payouts from an annuity:
- Withdraw money when you want (withdrawals are taxed as income and may have an added 10% tax if you are younger than 59½).
- Elect to annuitize. Annuitization converts your annuity into a guaranteed income of regular payments. Your payments can be fixed or variable amounts and last for life or a specific period.1 Once annuitized, you usually cannot make extra purchases or withdrawals.
Advantages of Annuities
Annuities can be a beneficial tool that can ensure a stable and predictable income stream in retirement.
- Guaranteed Income: Annuities may provide a reliable income stream, which helps manage expenses in retirement.
- Tax-Deferred Accumulation: Taxes are only paid upon withdrawal, so earnings grow tax-deferred.
- Death Benefit: Some annuities provide a guaranteed death benefit.
- Protection from Market Downturns: Fixed annuities prevent principal loss, providing stability and peace of mind.
It’s essential to understand the many aspects and options when buying an annuity, including the fees and expenses that annuities may incur. You should consider your financial goals and risk tolerance. Consulting a financial professional can help you understand the details of annuities and ensure they fit within your broader retirement plan.
1Guarantees provided by annuities are subject to the financial strength of the issuing insurance company. Annuities are not FDIC or NCUA/NCUSIF insured; are not obligations or deposits of and are not guaranteed or underwritten by any bank, savings and loan, or credit union or its affiliates; and are unrelated to and not a condition of the provision or term of any banking service or activity.